
 |
Syllabus
Instructor:Name: Dr. Levent Yilmaz
Auburn Modeling and
Simulation Laboratory of the M&SNet
|
 |
|
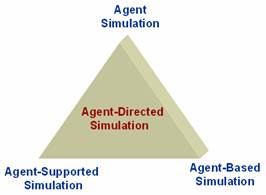
Course Description: This course has dual objectives: (1) acquiring modeling and simulation skills to develop simulation-based solutions to analyze complex systems that can be modeled by discrete event methodology and (2) ability to use software agents to not only represent intelligent entities within simulation models but also to enhance modeling and simulation environments. Agent theoretic fundamental model design principles and conceptual frameworks are overviewed. The course covers the entire simulation development life cycle including problem formulation, system and objectives definition, conceptual modeling, model design, implementation, experimentation, and credibility assessment. Each student involves in a research project to develop a research paper.
Course Objectives: Having successfully completed this course, students will be able to (1) solve complex problems by way of using computational agent theory and methodology under the discrete-event simulation framework, (2) simulate agent systems using a discrete-event model development environment (i.e. DEVS), (3) demonstrate advanced knowledge in the modeling and simulation of agent technologies such as negotiation, coordination mechanisms, auction mechanisms, coalition formation etc., and (4) participate in agent-based simulation model design and development projects.
Recommended Texts:
There is no required text for this course. A number of selected papers will overviewed and discussed in class. The following are the recommended texts.
Course Requirements:
1. Final Examination (20%) – Final exam will be a closed-book comprehensive exam. 2. Project (40%) – There will be one substantial research project. The assignment entails the proposal as well as development of an agent-directed simulation project. Each student is responsible for sketching project’s requirements, identifying the critical simulation design issues, and performing a agent-directed simulation study. Students will be required to produce design documentation, simulation implementation, and present their results. Additional information concerning the project will be presented in class. 4. Research Paper (20%) – The technical research paper will be based on the agent simulation project. 5. Participation (20%) – Students are expected to participate in class discussions, make presentations based on the assigned papers and group projects. |
Grading:
|
Grade Distribution |
Grading Guidelines
|
|
Final Exam: ………………….. 20% Project: ........……… 40% Participation: ……………….. 20% Research Paper: ……………………… 20% |
90-100 A 80-89 B 70-79 C 60-69 D below 60 F |
|
Accommodation Policy: If you need special accommodations, please contact me during the first week of classes.
Policy on Academic Integrity and Plagiarism: Academic integrity is central to the learning and teaching process. Students are expected to conduct themselves in a manner that will contribute to the maintenance of academic integrity by making all reasonable efforts to prevent the occurrence of academic dishonesty. Academic dishonesty includes, but is not limited to, obtaining or giving aid on an examination, having unauthorized prior knowledge of an examination, doing work for another student, and plagiarism of all types. Plagiarism is the intentional or unintentional presentation of another person’s idea or product as one’s own. Plagiarism includes, but is not limited to the following: copying verbatim all or part of another’s written work; using phrases, charts, figures, illustrations, or mathematical or scientific solutions without citing the source; paraphrasing ideas, conclusions, or research without citing the source. |
Schedule:
|
Date |
Topics |
| 1/11, 13 |
Orientation to
course. What is simulation? The lifecycle of a simulation study.
Discrete-event models and their simulators.
|
| 1/18,20 |
Introduction
to agent-directed simulation. Application areas of agent simulation.
Introduction to DEVS for the simulation of agent
systems.
|
|
Agent-Based Modeling |
|
| 1/25, 27 |
Characteristics and types of agency (rational, social, interactive, adaptive agency). Agent micro-architectures: reactive and hybrid agent models, practical reasoning agents. Agent simulator design (An agent interpreter).
|
| 2/1,3 | Interactive Agency. Modeling action and agent
behavior. Tropistic and hysteretic agents. Rational agency and modeling of cognitive
agents. Reactive vs. intentional undertaking of actions in agent system
simulations
|
| 2/8,10 | Modeling agent
interaction protocols: coordination, cooperation, and collaboration in agent systems.
|
| 2/15, 17 | |
|
Simulation of Agent Systems |
|
| 2/22, 24 | Agent simulation in social sciences, economics, biology, human behavior, engineering, political science etc. (Class presentations and discussions on selected topics and papers) |
| 3/1, 3 | |
| 3/8,10 | |
| 3/15,17 | |
| 3/22, 24 | |
| 3/29,31 (Spring Break) |
|
|
Agent-Supported Simulation |
|
| 4/5,7 | Agents in support of simulation interoperability, agents for intelligent
assistance - information sharing and coordination, agents in simulator
design (multimodel simulators, multisimulation).
|
| 4/12,14 | Experimentation with stochastic models
|
| 4/19,21 | Project and research paper presentations. |
| 4/26,28 | Project and research paper presentations. Research Topics in Agent-Directed Simulation. Course overview |
| 5/10 | Final Exam |